Cyber attack
survival guide
by Maija Palmer


Have you
been hacked?
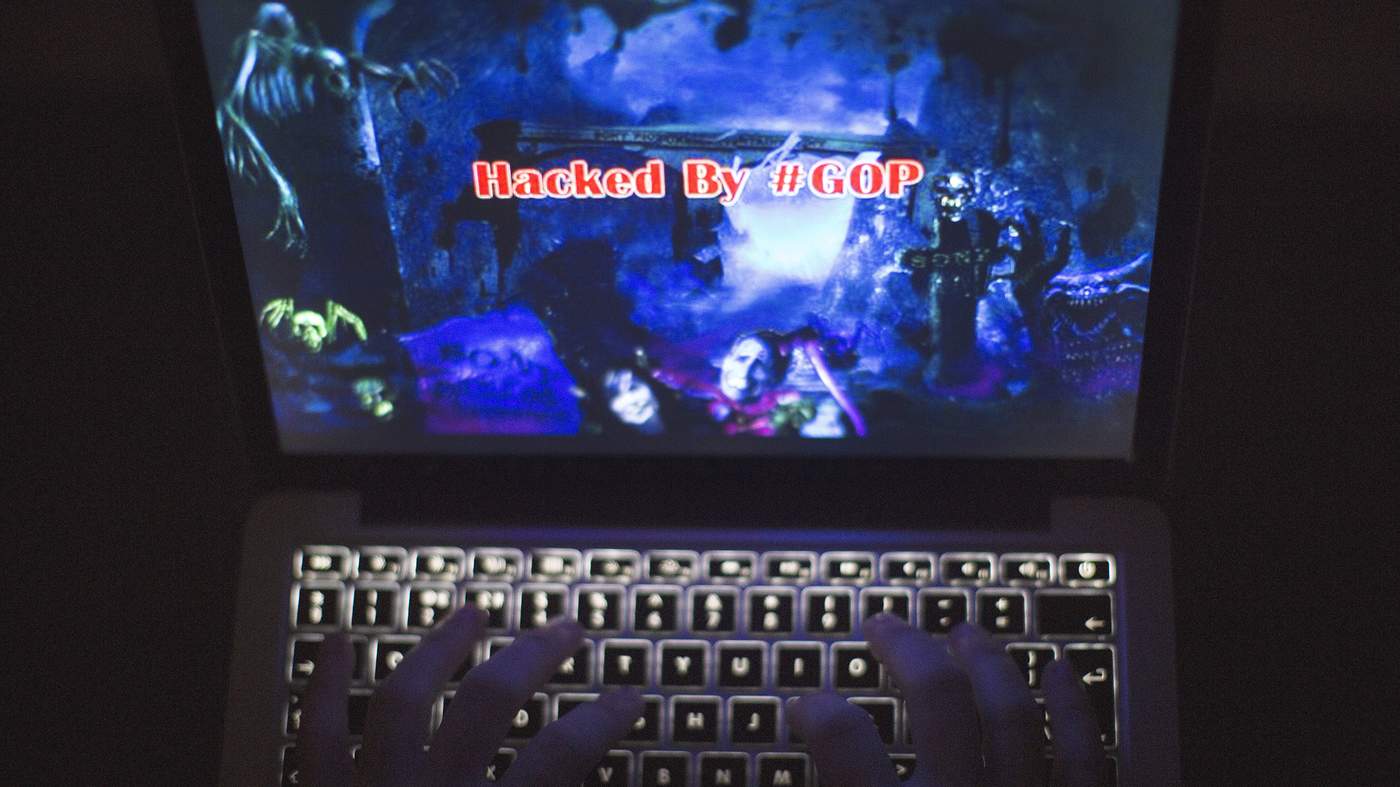
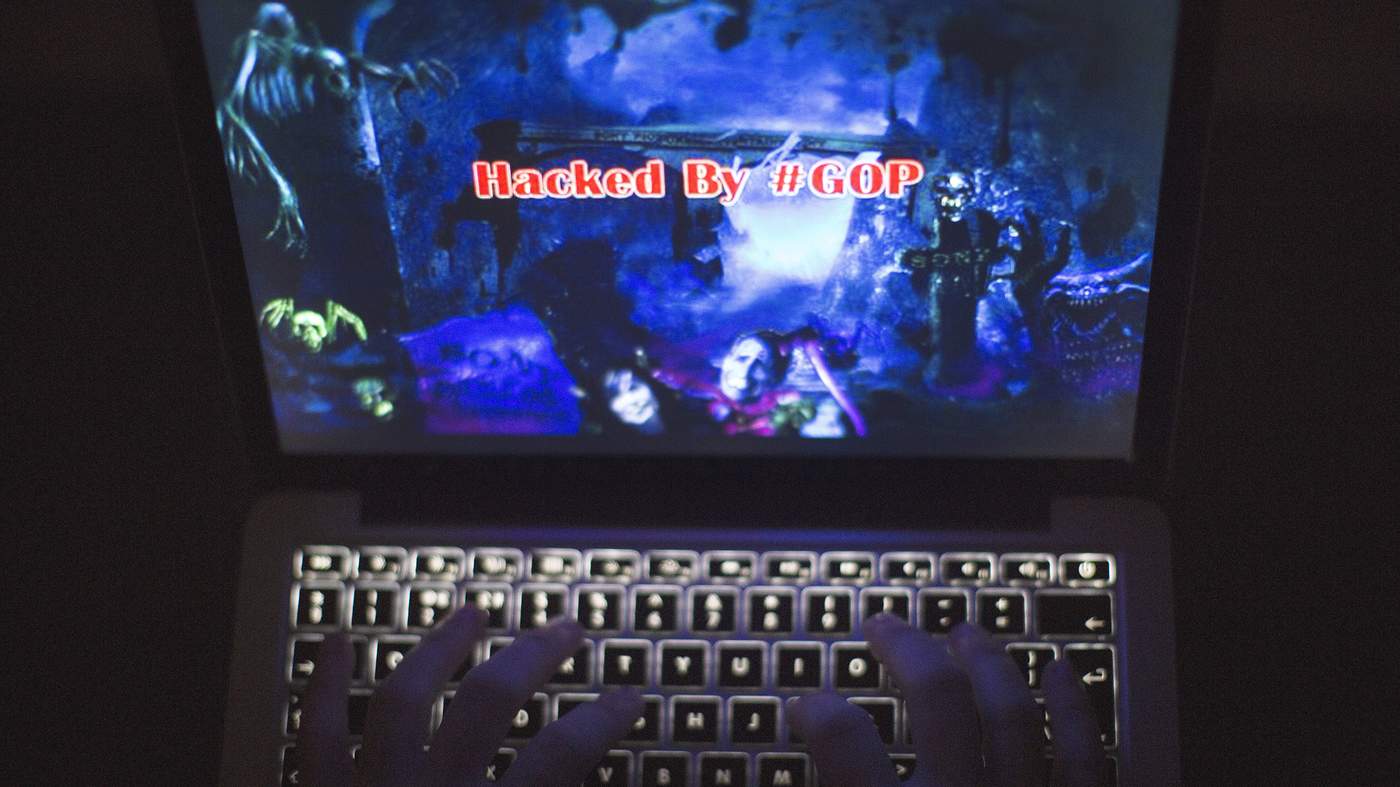
Sometimes a hack is obvious. When Sony Pictures employees arrived at work on the morning of November 24 2014 they found their computers were inoperable and the screens displayed a creepy-looking red skull with the message: “Hacked by #GOP”.
More often, attacks are harder to recognise. For TalkTalk, the UK telecoms company that discovered on October 21 2015 that it had been hacked, the truth sank in much more gradually. Dido Harding, the chief executive, explained in a television interview two days later that by “lunchtime all we knew was that our website was running slowly and that we had the indications of a hacker trying to attack us”.
It took TalkTalk 36 hours after discovering the hack to release a statement saying it had been attacked and warning customers that their data may have been compromised — a delay for which it would later be criticised.
Most hacks follow warnings that were overlooked: emailed tip-offs, both internal and external, about a potential security risk that were never read, phone calls that were ignored.
Richard De Vere, a consultant at cyber security company The AntiSocial Engineer, says he contacted TalkTalk about a separate problem two weeks before the hack was made public. He had discovered that several self-hosted websites that used the company’s talktalk.net domain were infected with malware and could be used to aid social engineering attacks, where criminals trick people into revealing confidential information.
He felt TalkTalk did not take him seriously. “After a week of emails and calls, nothing seemed to happen,” he recalls. Frustrated with the lack of progress, on October 9 Mr De Vere published a blog making the matter public. TalkTalk’s head of IT then contacted him via LinkedIn and the company decommissioned the talktalk.net domain.
‘Most of the time these calls are not serious’
Mr De Vere says he later alerted TalkTalk to the main attack. This time the company’s senior technicians were listening.
John Smith, who worked as a chief information security officer (CISO) for private sector companies for 14 years, says IT security professionals often do not give tip-offs the necessary attention straight away. “Most of the time these calls are not serious, but you need to pay attention every time,” says Mr Smith (who is quoted under an assumed name to protect the identity of the organisations he has worked for).
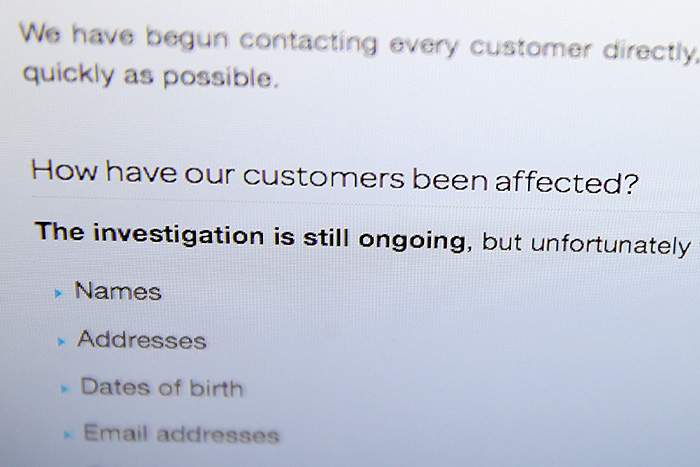
Verifying that there really has been a breach can be difficult, says Tammy Moskites, chief information officer and CISO at Venafi, a Utah-based IT security company. Leaked credit card numbers, for example, can be checked. But if a mix of types of information appears to have been exposed — for example, emails, credit card numbers and passwords — it can be difficult to know for sure whether this is due to an attack on a company’s computer systems or if information has leaked in other ways. These include customers falling victim to a scam or another company, which stores similar customer data, being attacked.
STORY CONTINUES AFTER ADVERTISEMENT
Immediate response

Once the hack is confirmed, things begin to move very quickly. “This is the ‘golden hour’ where every minute counts,” says Jamie Saunders, who leads the UK’s National Crime Agency’s efforts to fight cyber crime.
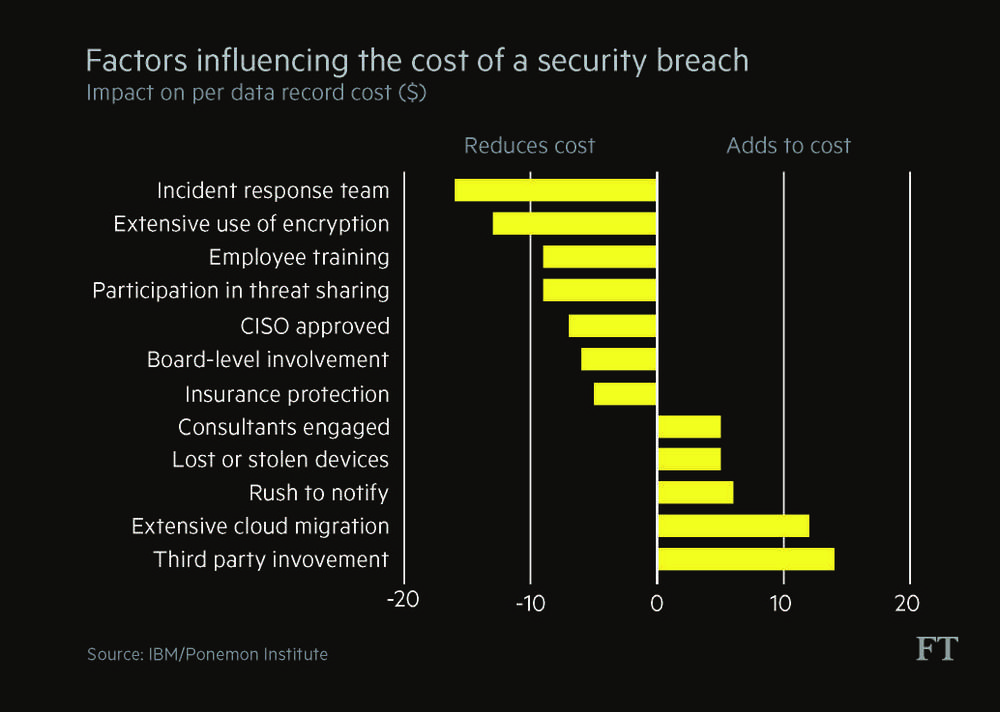
The company’s first call should be to its incident response unit — a dedicated team trained to deal with attacks. This can be an in-house group or an external company on retainer. Having an incident team makes the biggest difference in reducing the cost of an attack, says Larry Ponemon, chairman and founder of the US-based Ponemon Institute, a security research group. However, only 29 per cent of UK companies have formal written cyber security policies, according to a 2016 UK government survey.
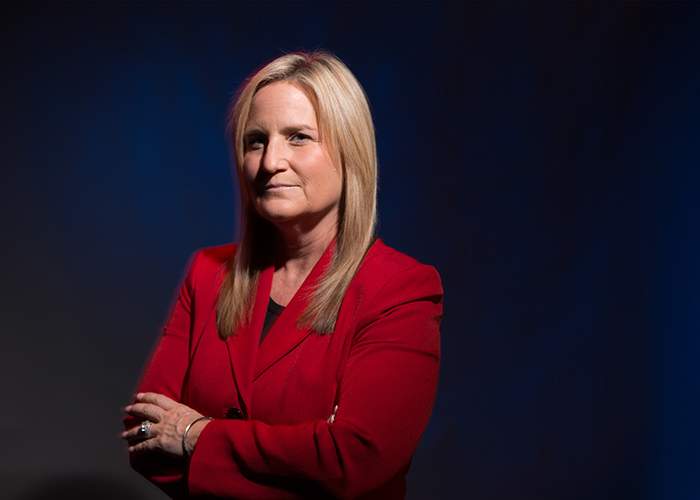
“Detecting [a cyber attack] early is key,” says James Hatch, director of cyber services at BAE Systems, who advises companies on how to defend themselves. “It could be the difference between losing 10 per cent of your [computers] and 50 per cent.”
“You are trying to get everyone into the war room very quickly,” says Mr Smith. “You have a plan for this kind of incident, you may have practised it. But right now you are wondering if the right people are reachable. It always seems to happen at the start of a long weekend and no one is around.” Having 24-hour-a-day, seven-day a week rota for staff can be crucial, he says.

James Hatch, director of cyber services at BAE Systems, says it is critical to detect cyber attacks early
JPMorgan, for example, did not have a CISO when it suffered a security breach in 2014. Neither did Target, the US retailer, when it was hacked in 2013, exposing 40m customer records. The cyber attack against Sony Pictures also came at a particularly vulnerable time for the company, when a new CISO was less than three months into the job.
“For the first few hours you are just trying to find out what happened. Are the hackers still in your system? Can you see data still being transferred out? Some companies panic and want to just pull the plug out of the socket at that point to protect their system, but you cannot simply switch off. It sends a bad message to the outside world and impacts business operations,” says Mr Smith.
‘You are actually wetting your pants at this point. Your goal was to prevent something like this happening and that hasn’t worked. No one wants this kind of blot on their career.’
It is reasonable for executives to be anxious. Both Gregg Steinhafel and Beth Jacob, Target’s former chief executive and ex-information officer respectively, lost their jobs following the data breach. The average tenure of a CISO at a company is a little more than two years, according to the Ponemon Institute. This is partly due to the fact that these professionals are in such high demand, but also due to job insecurity of those in the role.
STORY CONTINUES AFTER ADVERTISEMENT
Can we keep it a secret?

At this stage, companies are often most concerned about making sure news of the hack does not spread. “You want as few people as possible talking about it,” says Mr Smith. “You call the CEO and tell him to keep his mobile phone switched on. You issue a gag order to everyone else.”
There will be difficult discussions about which external bodies — from law enforcement and regulators to customers — must be told. “Nobody wants anyone else involved,” says Mr Smith.
Another consideration is not wanting to let the hackers know they have been discovered, says Ms Moskites, the Venafi CISO. “If the hackers are still inside your system you may have to be creative about how you communicate if you don’t want to alert them.”

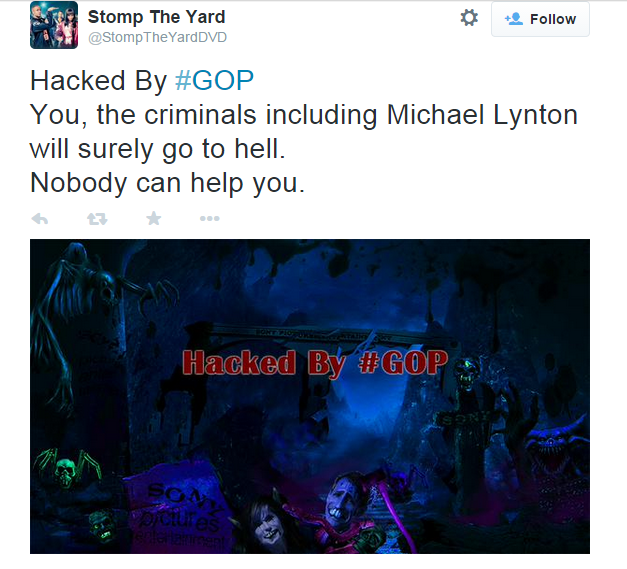
But complete secrecy may not be an option. If the cyber attack came from hacktivists who want to make a political statement, news is probably already leaking out. During the Sony hack, several Sony-related Twitter accounts were taken over and posted a picture showing Michael Lynton, chief executive of Sony Pictures, in an eerie environment, surrounded by skeletons and gravestones.
Most states in the US require companies to notify their customers, immediately or without unnecessary delay, if their personal data have been lost. In Europe, some countries, including Germany, Austria, Norway and the Netherlands, have introduced similar laws. EU data protection regulation, due to come into force in 2018, will extend this requirement across all member states. Under the new rules companies can face hefty fines for failing to disclose a loss of data.
Even before the new rules come in, European telecoms companies are obliged to notify regulators about data breaches and if a company holds data on US citizens, it may be required to disclose the breach in the US. Disclosure rules in each US state differ slightly.
“It is a potential nightmare,” says Antonis Patrikios, partner at Fieldfisher, a UK-based law firm. “Companies are just starting to realise how complex this can be. It is important to think about your notification strategy before an incident happens. If you leave this to be decided when you are in the middle of dealing with an attack it can be a lot more complicated.”
The company must also consider whether to call the police. Some 2.5m cyber crime offences take place in the UK each year, according to estimates by the government’s Office for National Statistics. “Almost every large organisation will have some kind of breach each year,” says Mr Hatch of BAE Systems. Only a fraction of these are ever reported to the authorities.
“We are seeing companies that are more willing to engage us, but that is not the majority,” says Mr Saunders of the UK government’s National Cyber Crime Unit. “Some have had bad experiences. There are plenty of disincentives for companies on reporting. They don’t want PC Plod to come in and stop them from working. We are trying to become more sensitive to business priorities.”
In the TalkTalk case, the police became involved immediately after the hack was detected, but there was tension over priorities.
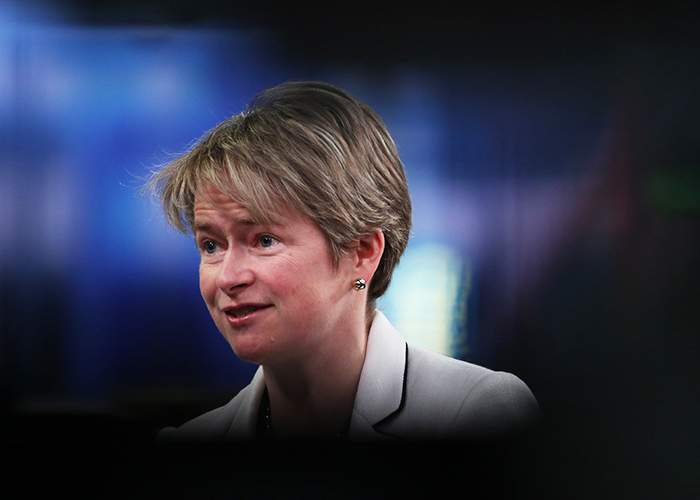

“The advice we received from the Metropolitan Police was not to tell our customers,” said Baroness Harding, TalkTalk’s chief executive, in a testimony to the UK government’s Culture, Media and Sport Committee. “I totally understand why the police wanted us to stay quiet because they have a different objective. They want to catch the criminals. We had some constructive discussion with them … on how to marry the conflicting objectives.”
Mr Smith admits he, like many corporate CISOs, believes pursuing criminals is a waste of time. “It is difficult to ascertain exactly where the hack came from — they are typically routed through so many countries,” he says. “Even if you found the computer that the attack was coming from, would you know you had really found the right people? If you have your business hat on you don’t really want to spend time on that.”
The first
seven days


The company’s IT security team will be working around the clock at this stage. Some will have been in the office for 30 hours straight after the hack was discovered, surviving on takeaway pizza and strong coffee.
The work will be tedious, often involving going through millions, if not billions, of log entries to find out exactly when and how the breach took place.
The company should brace itself for unpleasant surprises — starting with finding out just how long the hackers have been in the system. “As you investigate you suddenly realise, ‘Oh my God, we were breached in April and it is now October — what happened?’” says Ms Moskites.
It takes companies an average of 229 days — more than seven months — to discover a malicious attack, according to research by the Ponemon Institute. “It is not unusual for a problem to have been there a long time,” says Dave Palmer, director of technology at Darktrace, a UK-based cyber security company. “In one case we found that the problem had been there for eight years.”

‘You need a war room that has a washroom connected to it and a couple of sofas that people can sleep on. The team will bring in sleeping bags’
The way in which the company was breached may also be a surprise. Hardware that was not even considered an issue may have been the weak point. Mr Palmer gives the example of a law firm that discovered its video conferencing system had been compromised and had been livestreaming all the conversations to an unknown location from the boardroom for a week.
Part of the challenge is keeping up security for an increasingly complex network. The IT team may have decommissioned old servers and simply forgotten to disconnect a couple. “It is like forgetting to get the old food from out of the back of the fridge,” says Ms Moskites.
The attack may also have been embarrassingly simple. Former hackers themselves say that the skill level in many hacks is not high. “There is this joke in the hacker community that companies always say they got hit by an ‘advanced persistent threat’ to make it sound like it was something very complicated,” says Lauri Love, a British hacker who is accused of breaking into Pentagon computers and is currently fighting extradition to the US. Mr Love is now part of Hacker House, a social enterprise start-up that aims to encourage young computer experts to use their skills for positive ends.
“There is a lot of code running on computers and some of it is kept up-to-date ... and some of it is not up to scratch. If you are persistent you will find it,” Mr Love says.

“It isn’t about Russia, China or GCHQ [the UK’s information security agency] launching outlandish, Mission Impossible-style attacks,” agrees Mr Palmer. “Mostly it is about routine, indiscriminate attacks.” Cyber attack tools can be bought on the black market by non-experts and criminals will often use these to target a wide range of companies, seeing which businesses are most vulnerable.
In its review of the TalkTalk hacking case, the Culture, Media and Sport Committee noted that it was “no longer a defence” for a company to claim to be unaware of “established and in some cases routine” forms of cyber penetration. The committee recommended introducing an escalating series of fines if companies are caught out by basic attacks.
How much will it cost?

The average cost of a data breach is $4m, according to security researcher Mr Ponemon, or around $158 for each compromised record. In fact, the figure can vary considerably. Sony estimated in early 2015 that the combined cost of investigating its hack and offering remediation would be $15m, after recovering some losses from insurance. It will also pay up to $8m to settle a lawsuit brought by former employees whose personal data were stolen.
By the end of 2015, according to Target’s financial statements, the company recorded costs of nearly $291m related to the 2013 data breach, including crisis communications, the forensic investigation and law suits.
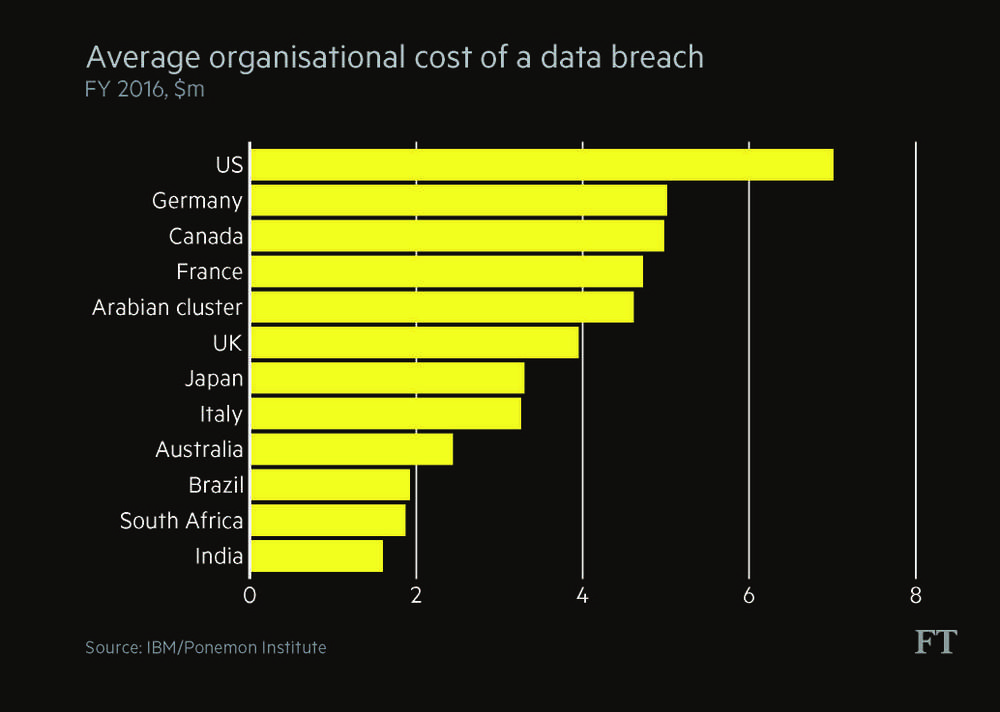
The longer it takes to find a hack, the more costly it is to deal with. If a data breach can be identified within 100 days the cost to the company will on average be $3.2m, compared with an average of $4.4m to deal with hacks found after 100 days, according to the Ponemon Institute.
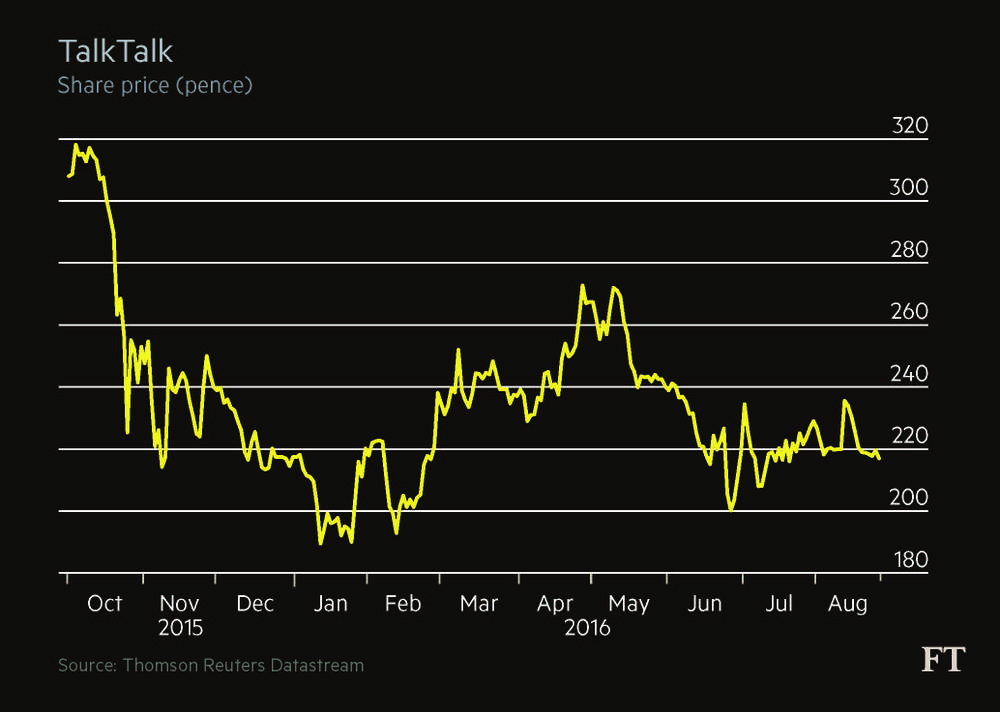
TalkTalk has so far estimated that the October 2015 cyber attack will cost about £60m ($78m) to rectify. The company’s business has also taken a hit. Its pre-tax profit for 2016 fell to £14m, compared with £32m last year as about 100,000 customers left.
TalkTalk's shares fell sharply in the aftermath of the hack and were down 30 per cent nearly a year later. The good news for companies is that the share price tends to recover relatively quickly following a cyber attack.
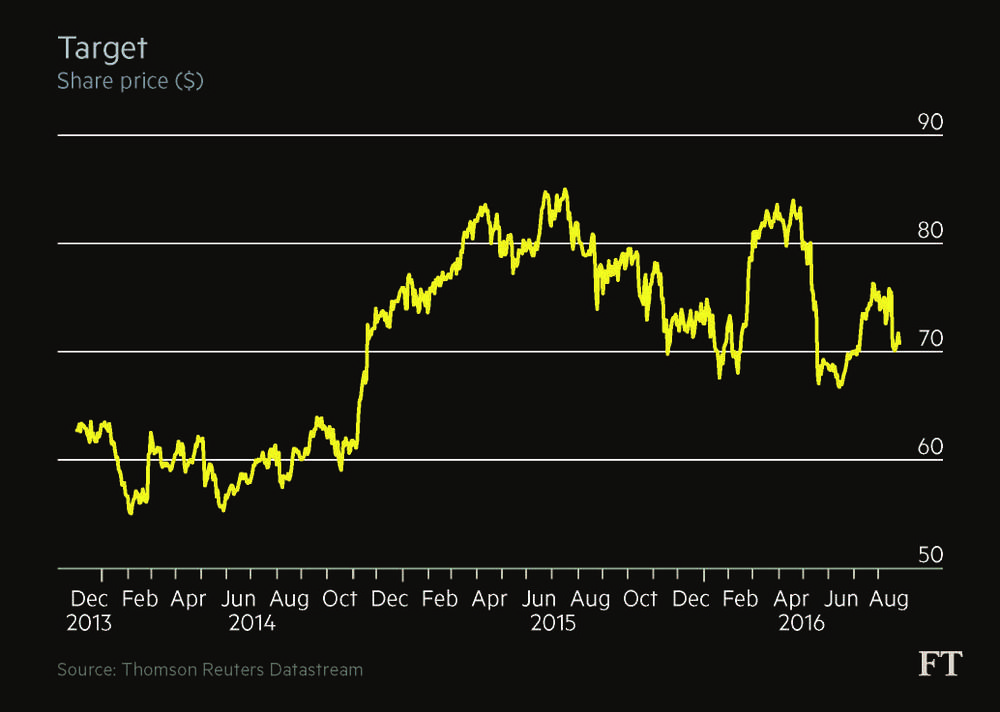
Target, for example, saw its share price fall sharply in the immediate aftermath of the December 2013 attack. Nine months later, however, it had recovered. Even revelations that the company would have to pay more than $118m to settle lawsuits filed against it by banks, card issuers and customers failed to depress the share price. Sales growth and other corporate news gradually began to outweigh news of the hack.
“People have short memories,” says Mr Palmer of Darktrace.

Dave Palmer, director of technology at Darktrace, says the impact of a hack on a company’s share price is often shortlived
Insurance becomes a key consideration at this point. Insurance can cover the cost of the forensic investigation, the cost of notifying customers affected by the attack and even the cost of lawsuits. But companies must check carefully what they are buying, warns Sarah Stephens, head of cyber, technology and media at JLT Speciality, a UK-based insurance broker.
‘Cyber insurance can cover the cost of dealing with the crisis, but not the extra work needed to fix the company’s security flaws’
“It can cover lost income from an attack, but not the longer-term impact on reputation,” says Ms Stephens. If cyber criminals transfer money from company accounts, this would not be covered by cyber insurance — but it should be covered under a different, criminal insurance policy.
Documents leaked as part of the Sony Pictures hack suggest the company had at least $60m worth of cover at the time and Mr Lynton, the chief executive, told reporters the costs would be within insurance limits.
Target was less lucky. Its cyber insurance policy will cover just $90m, less than a third of the costs. “They did have cyber insurance — just not enough,” says Ms Stephens.
Making sure it does not happen again
After the hack, the company will typically have a serious review of its IT security. Meanwhile, the CISO, provided they are still in the job, will go on a shopping spree. “If you asked for $1m for a project before the hack and were turned down, you will now get $2m — no questions asked,” says Mr Smith, the former CISO.
“You do get more money. I have seen that quite a bit. But you have to move quickly because there are peaks and valleys in the spending and the further you get from the incident the more it will start to trickle off again,” says Ms Moskites, CISO at Venafi.
Following the 2013 hack, for example, Target built a new cyber centre, bringing together all its IT security teams.
But buying in technology will not on its own make companies safer. A complete change of tactics may be needed. TalkTalk is working not only with conventional security companies such as BAE Systems, but is looking for new ways to test its systems.
Mr Love of Hacker House says companies need to go back to basics. For example, they should review how reliant they are on third-party code they have not written themselves, which is probably more vulnerable. Companies must also train employees to become more vigilant and suspicious of emails that look unfamiliar, he says.
Collaboration with other security professionals could also be improved. One idea that companies are increasingly exploring is so-called bug bounty programmes, where the company pays outsiders who notify it of security flaws. Big US technology companies such as Google and Facebook have operated such programmes for several years. More recently platforms such as Bugcrowd and HackerOne have created places where any company can ask independent security researchers to test its systems.
When is it over?

“After the first week you have a postmortem,” says Ms Moskites. “But when is it done? Just because you fixed the inside of the system, it doesn’t mean it is over. There is brand reputation and possibly many people who are impacted.”
The fallout from the Sony Pictures hack was widespread. Employees had their social security numbers exposed and will have to be vigilant about identity theft for the rest of their lives. Leaked emails caused embarrassment to the studio, fuelling weeks of showbiz media stories. It ultimately led to the departure of Amy Pascal, co-chair of the film studio.
Nearly three years after its attack, Target is still dealing with lawsuits.
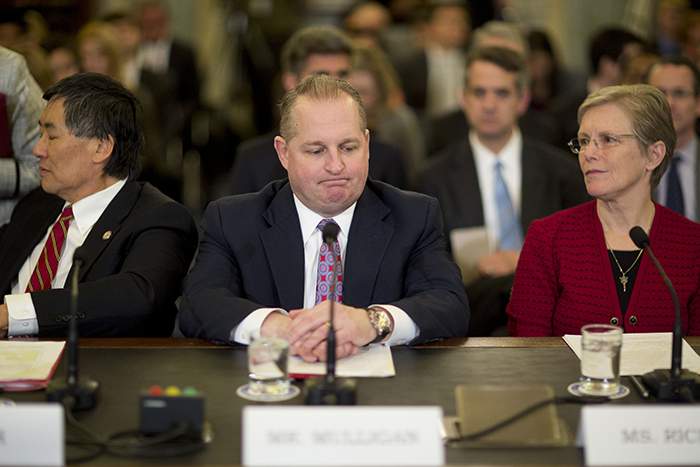

Target chief financial officer John Mulligan testifies before the US Senate Commerce Committee in March 2014
TalkTalk says it is starting to see customer numbers growing again, but the investigation into the incident is continuing. London’s Metropolitan Police has so far arrested six people in connection with the data breach, ranging in age from 15 to 20 at the time of arrest. The young ages suggest the hackers were cyber vandals rather than career criminals.
The FBI and US President Barack Obama officially linked the Sony Pictures hack to North Korea, although some security professionals say the evidence presented by the FBI was scant. There has also been speculation it could have been an inside job by disgruntled employees. No one has yet been arrested in connection with the hack.
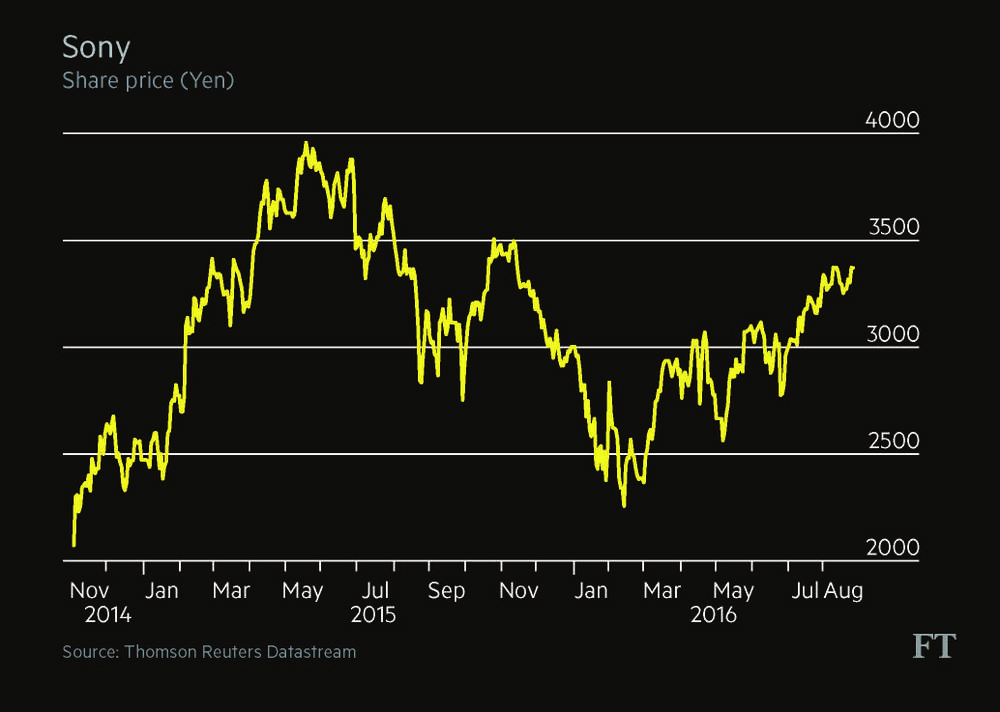
Despite the leak of highly embarrassing emails, Sony’s share price was relatively unaffected by its November 2015 hack
The reality is that there is often no closure. “People think it is a problem that can be fixed and you move on. But it is not like a bug,” says BAE’s James Hatch. “The attackers just have to be lucky once. The defenders have to be lucky all the time.”
To read more on cyber security, subscribe to FT.com.
Credits
Written by Maija Palmer
Edited by Owen Walker
Design by Alan Knox
Video and photography by Charlie Bibby, Anna Gordon, Anne and Michael LoBiondo
Graphics by Graham Parrish, Kari-Ruth Pedersen
Production by Ruth Lewis-Coste
Additional photography: Bloomberg, AFP, NuPhoto, Getty Images, Reuters
Built with Shorthand
